Kingdom Protista: Characteristics and Examples
Reasons for a separate kingdom protista
- Basically the kingdom protista is defined by principle of exclusion i.e. all the members have certain characteristics that exclude them form all other four kingdoms. The kingdom protista is composed of a large number of primarily aquatic organisms. These organisms have different body forms, types of methods of reproductions, modes of nutrition and life style. It is difficult to characterize them in a single group. There was difficulty in placing these organisms any of the kingdoms. So, all such organisms are placed in protista.
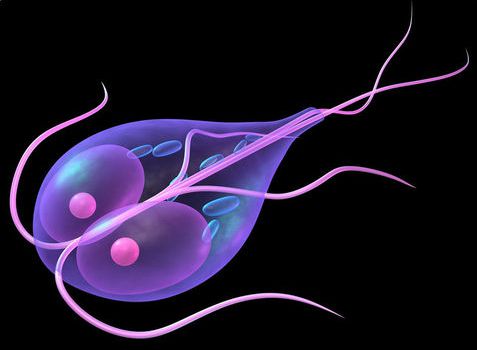
- There is another reason of placing them in a separate kingdom. All the protists are eukaryotes. They have evolved from prokaryotes. All other eukaryotic kingdoms have their evolutionary origin in protista (evolved from protists). The protists are ancestors of all other eukaryotic organism. So it becomes difficult to place them any of the kingdom. The other eukaryotic kingdoms, Plantae, Animalia, and Fungi have evolved from protists in different way.
- The protists are unicellular, colonial or simple multi-cellular organisms. The protists are eukaryotes like other three eukaryotic kingdoms, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. But the protists do not form blastula and embryo which are formed by animals and plants. They are also different from the prokaryotic kingdom Monera. So they are placed in separate kingdom.
Historical Perspective
Following biologist played their role in the formation of Kingdom Protista:
1. John Hogg
He proposed the kingdom Protoctista for microscopic organisms in 1861.
2. Ernst Haeckel
He suggested for creating the kingdom Protista in 1866. He included in this kingdom bacteria and all other microorganisms which did not fit in plant and animal kingdom like amoeba. However, he separated the blue green algae and bacteria (prokaryotes) from the nucleated protists. He placed them in a separate group called Monera, within the kingdom Protista.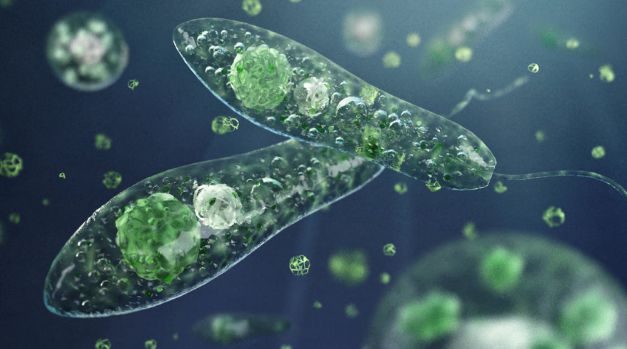
3. Herbert Copeland
He separated the prokaryotes from the Protista and raised the prokaryotes (Monera) to the status of kingdom in 1938.
4. Robert Whittaker
He formed five kingdom systems in 1969. He placed only unicellular eukaryotes in Protista.
[wp_ad_camp_3]
5. Margulis and Schwartz
They modified the five kingdom system in 1982. They also included colonial and simple multicellular eukaryotes in Kingdom Protista. Now kingdom protista have all unicellular, colonial and simple multicellular organisms. Protists or Protoctista is one the five kingdoms.
Diversity Among Kingdom Protista
Evolution has produced diversity in the Protista. They show diversity in following characters:
- Size and structure.
- Means of locomotion.
- Ways of obtaining nutrients.
- Interactions with other organisms.
- Habitat
- Mode of reproduction.
Due to this diversity most biologists take protists as polyphyletic group of organisms. The protists do not have single common ancestor. Margulis and Schwartz have formed 27 phyla of all the diverse organisms of the Protista.
[wp_ad_camp_4]
Major Groups of Kingdom Protista
Protista has following four major groups:
- Protozoans (single celled).
- Unicellular algae.
- Multicellular algae.
- Fungus like protists: Slime molds (Myxomycotes) and water mold (oomycotes).




I’ve been browsing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never
found any interesting article like yours.
It is pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if
all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the net
will be a lot more useful than ever before.